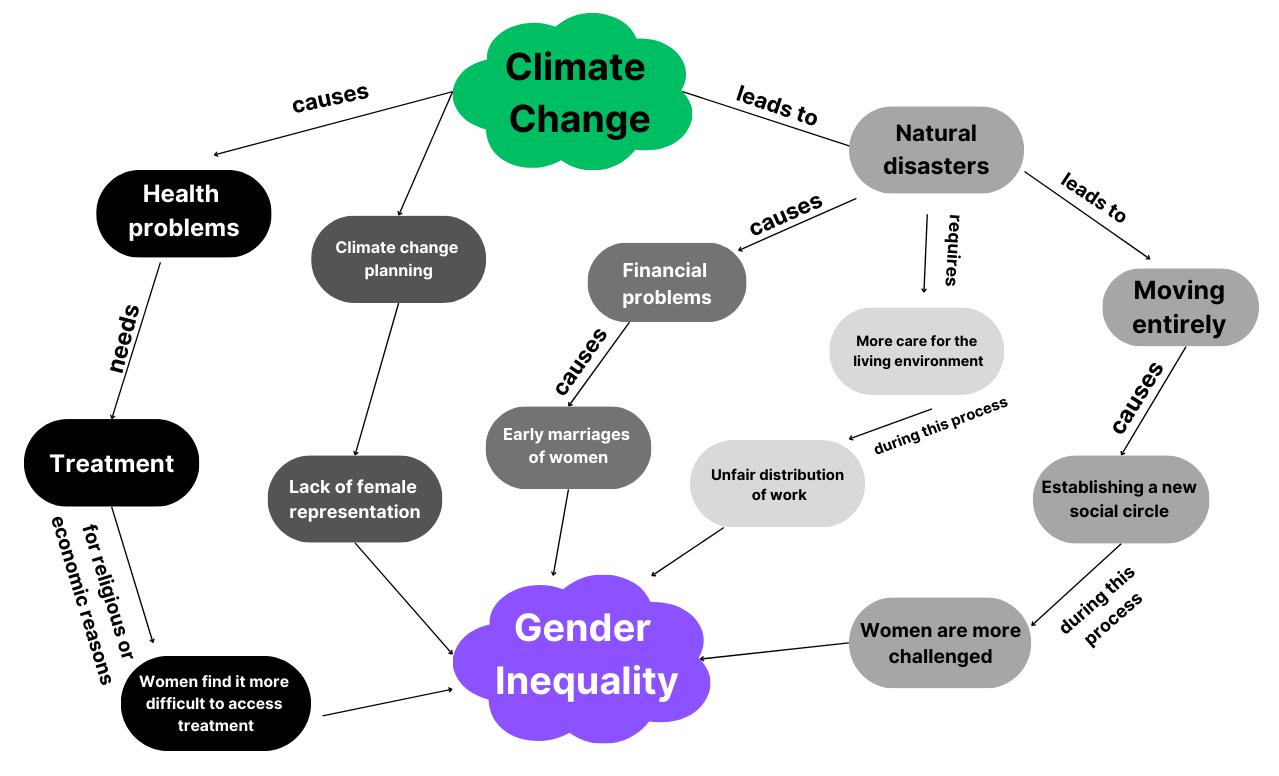
The relationship between gender inequality and climate change
While gender inequality brings challenges for women and other marginalized communities, climate change aggravates the impacts of these challenges, leading women and other marginalized communities to be disproportionately affected by climate change.
- In societies where gender inequality is widespread, women who lack access to education often turn to agriculture. Climate-change-driven issues such as drought, decreasing water resources, extreme weather events, and coastal flooding can threaten farming areas and affect women whose livelihoods depend on agriculture. As soil yields decline due to climate change, women earn less income despite working longer hours. [3]
- Climate change causes increased temperatures on Earth and leads to hotter environments. Being in an uncomfortably hot environment might result in feelings of irritability and aggression. These negative feelings may trigger violence perpetrated by men against marginalized communities, which is an outcome of a complex relation between heat and social norms that cast "aggression" and "dominance" as masculine traits for men. [4]
- Climate-change-driven disasters may cause people to lose their jobs and put them on a mission to find new jobs. Due to gender inequality, marginalized groups may struggle with getting employed more.